

What are the objectives of implementing this Ind AS?
The objective of this standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment of inventories. It provides guidance on cost formulas to ascertain the value and determines some exceptions in which different valuation methods shall be applicable.
Relevance of Ind AS - 2.
It defines the meaning of inventories, provide its measurement criteria, specifies the inclusions and exclusions in cost to be recognised as an asset and the amount to be carried forward until the related revenues are recognised.
What role does it play in the accounting framework?
It gives us the basis of recognition of inventories, techniques for valuation in different types of industries and also guide the treatments in cases where inventories are to be valued as per other standards in force.
What are the basic points that have to be kept in mind while implementing this Ind AS?
1. Exceptions to applicability of this standard:
2. Materials and other supplies held for use in the production of inventories are not written down below cost if the finished products in which they will be incorporated are expected to be sold at or above cost.
Key Paragraphs & their interpretations.
1. Definition of Inventories
Inventories are assets:
[Para 6]
2. Inventories shall be measured at the lower of cost and net realisable value where cost shall include all costs that are incurred to bring the inventories to their present location and condition and net realisable value refers to the net amount expected to be realised from sale in the ordinary course of business.
[Para 9 & 10]
3. Techniques for valuation of inventories for different types of industries:
Ind AS 2 recognises another two types of methods of valuation along with para 9&10.
[Para 22]
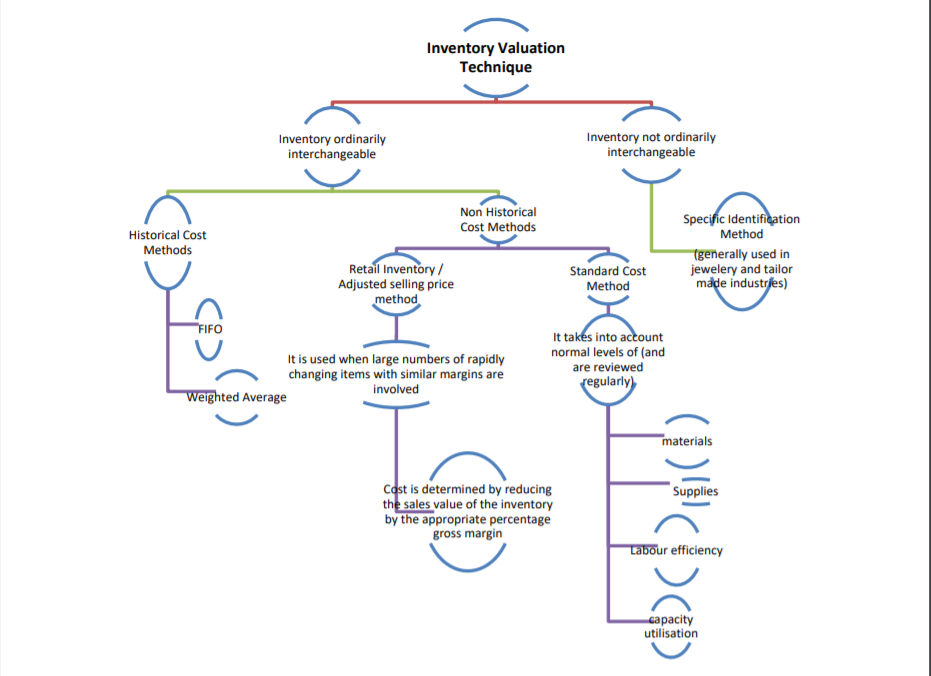
*Image extracted from ICAI's Publication
4. Inventories to be written down as expense and reversal of written down in certain circumstances. (Covered under compliance paragraph but gave reference here as it is an important paragraph)
[Para 34]
Compliance Oriented Paragraphs
1. All Types of inventories shall be valued either on FIFO or Weighted Average Method except when the inventories are not ordinarily interchangeable and goods or services are produced and segregated for specific projects, where the cost shall be assigned by using specific identification of their costs.
An entity shall use the same cost formula for all inventories having a similar nature and use to the entity.
[Para 23 & 25]
2. Disclosures Required as per Ind AS 2
3. Whenever inventories are written down by comparing it with net realisable value in a period, there can be some circumstances that can lead to increase in net realisable value in subsequent periods, the written down amount shall be reversed.This is one of the most important paragraphs of this standard which is not being followed properly even by large undertakings and therefore requires a greater cognizance.
[Para 34]
This is where our Ind AS 2 come to end, hope you liked the blog, any suggestions or improvements are accepted with great love, eager to hear from you in the comment section below
A quick Disclaimer, any information containing in this blog is not, in any aspect, to be considered as exhaustive explanation of the accounting standard; the key paragraphs, disclosure or carve outs are distributed and presented according to my personal judgement, ergo, optimum prudence should be maintained while complying with the Ind AS.